What to Do If Your Data Cable Overheats
It is normal for a data cable to feel slightly warm during charging or data transfer, as resistance generates heat when current passes through. However, if it becomes too hot to hold comfortably, it indicates an abnormal situation that requires attention.
First and most importantly: If the data cable or power adapter overheats abnormally, stop using it immediately and unplug all devices! Safety first.
Next, you can systematically troubleshoot and address the issue by referring to the flowchart below:
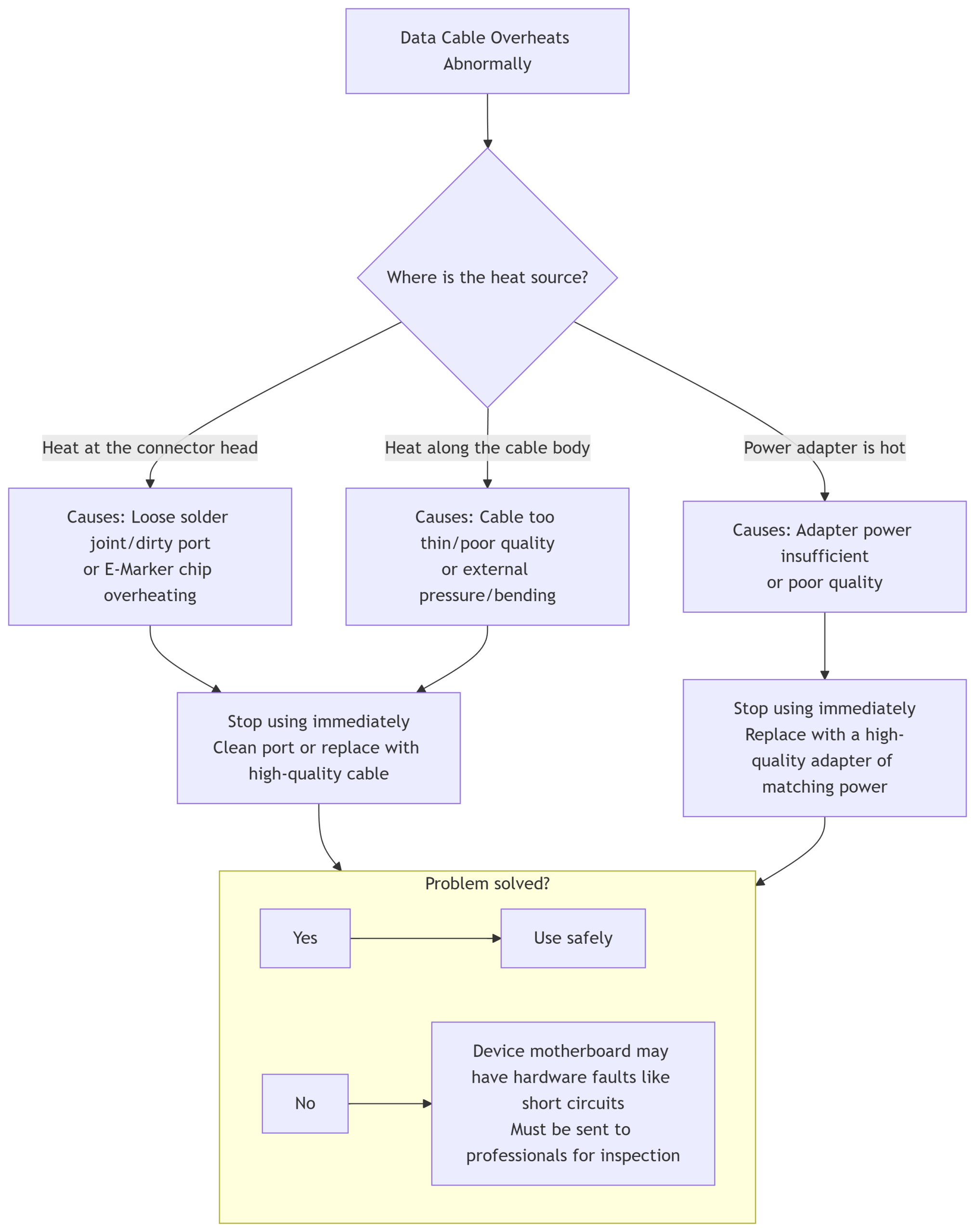
1. Physical Connection & Environmental Issues
-
Poor Connection: The plug isn’t fully inserted into the port, or there’s dust/debris inside the port, increasing contact resistance. Higher resistance leads to more heat generation.
-
Severe Cable Bending: The cable being pinched under weight, tied in knots, or overly bent can damage internal wires, effectively thinning the conductive pathway and increasing resistance, causing localized overheating.
-
High Ambient Temperature: Charging in direct sunlight or hot environments impedes heat dissipation, worsening overheating.
2. Power Delivery & Accessory Performance Issues
-
Fast Charging/High Current: Using fast charging significantly increases current (e.g., from 5W 5V/1A to 18W 9V/2A). According to Joule’s Law (Heat ∝ Current² × Resistance), heat generation increases quadratically with current.
-
“A Small Horse Pulling a Big Cart”: Using an underpowered or low-quality power adapter for high-power devices (like tablets or phones) forces the adapter to run at full load or even overload, resulting in low efficiency and converting electrical energy into heat.
-
Poor Cable Quality:
-
Inferior Conductor Material: Using Copper-Clad Aluminum (CCA) or impure copper instead of Oxygen-Free Copper (OFC) results in much higher resistance.
-
Conductor Too Thin: Cannot handle high current.
-
Lacking Shielding: Poor anti-interference capability.
-
No E-Marker Chip: The cable cannot correctly communicate its capabilities to the device, potentially causing the device to attempt drawing more current than the cable can handle.
-
3. Device-Related Faults
-
Faulty Device Battery: An aging or damaged battery has increased internal resistance, which can also cause the data cable and charger to heat up during charging.
-
Device Motherboard Short Circuit: A minor short circuit in the device’s charging port or on the motherboard’s charging circuit can cause abnormal current spikes. This is a very dangerous situation.
Summary & Final Advice
An overheating data cable is a warning sign prompting you to pay attention to charging safety.
-
Act Immediately: If overheating occurs, unplug it first.
-
Check Basics First: Clean the ports, ensure a secure connection, and avoid use in high temperatures.
-
Upgrade Your Accessories: This is the most effective solution. Invest in a high-quality power adapter with matching power output and a certified (e.g., MFi) high-quality data cable for your device. Their superior materials (e.g., OFC conductors, thick wires, good shielding) effectively reduce resistance, minimize heat generation, and protect your device’s battery.
-
Stay Vigilant: If the problem persists even with high-quality accessories, the issue likely lies with the device itself. Be sure to take it to a professional repair shop for inspection.
Safety is no small matter; don’t risk major loss for minor savings. The cost of a high-quality data cable is far less than replacing a phone battery or repairing a motherboard, and it is a crucial investment in home fire safety.







